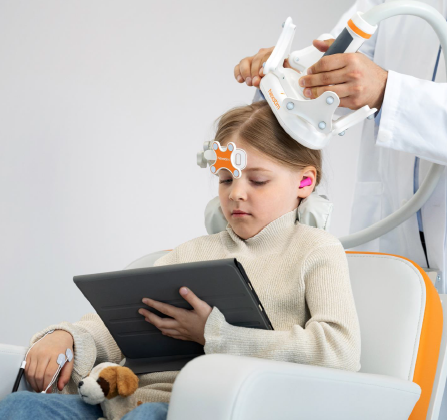
nTMS motor mapping in pediatrics
- The youngest reported patient successfully mapped was 8 weeks of age1
- Conducted in a child-friendly environment without the need for sedation
- May reduce the need for two-staged cases for invasive functional brain mapping1
nTMS language mapping in pediatrics
- The youngest reported patient successfully mapped was 4 years of age1
- Bilateral mapping captures inter-hemispheric functional reorganization1
- Multilingual mapping enables visualization of cortical regions associated with each language5
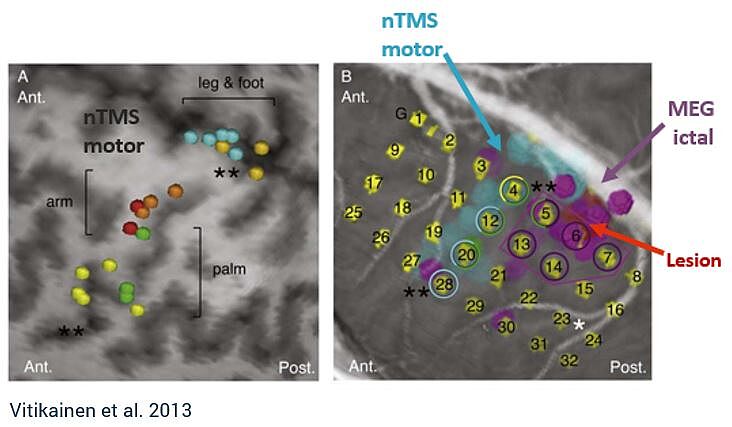
nTMS & MEG: A powerful combination in epilepsy surgery
Combining MEG and nTMS can yield powerful results. MEG can be used to investigate the onset zone for epileptic seizures, whereas nTMS can provide the margin to functional tissue, providing safe resection zones.4 This combination may reduce the number of patients required to undergo two-staged cases for invasive ECS monitoring, which carries significant health risks.4,6
“[MEG and nTMS] can be added to the standard preoperative work-up and may even hold a potential to replace the ECS in a subgroup of patients with epilepsy who have the suspected epileptogenic zone near the sensorimotor cortex and seizures frequent enough for ictal MEG.” - Vitikainen et al.
How nTMS is used in practice
See how one major epilepsy program in the US is using Nexstim nTMS motor and language mapping preoperatively to advance epilepsy care. This article also highlights how nTMS provides unique advantages to the pediatric population.
Learn more about how nTMS is used by our community of experts:
Yes, I would like to know more
References
1 Narayana et al., 2021. Clinical Utility of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) in the Presurgical Evaluation of Motor, Speech, and Language Functions in Young Children With Refractory Epilepsy or Brain Tumor: Preliminary Evidence, Front Neurol.
2 Raffa et al., 2019. The role of navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation for surgery of motor-eloquent brain tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg.
3 Pasichnik et al., 2022. Discrepant expressive language lateralization in children and adolescents with epilepsy. Ann Clin Transl Neurol.
4 Vitikainen et al., 2009. Combined use of non-invasive techniques for improved functional localization for a selected group of epilepsy surgery candidates, NeuroImage.
5 Gibbs et al., 2021. Presurgical language mapping in bilingual children using transcranial magnetic stimulation: illustrative case, J Neurosurg Case Lessons.
6 Onal et al., 2003. Complications of invasive subdural grid monitoring in children with epilepsy, J Neurosurg.
Indications for use
The Nexstim Navigated Brain Stimulation (NBS) System 5 is indicated for non-invasive mapping of the primary motor cortex of the brain to its cortical gyrus. The Nexstim NBS System 5 provides information that may be used in the assessment of the primary motor cortex for pre-procedural planning.
Nexstim NexSpeech®, when used together with the NBS System 5, is indicated for non-invasive localization of cortical areas that do not contain essential speech function. NexSpeech® provides information that may be used in pre-surgical planning in patients undergoing brain surgery. Intra-operatively, the localization information provided by NexSpeech® is intended to be verified by direct cortical stimulation.
The Nexstim NBS System 5 and NBS System 5 with NexSpeech® are not intended to be used during a surgical procedure.
The Nexstim NBS System 5 and NBS System 5 with NexSpeech® are intended to be used by trained clinical professionals.

